The Open Network (TON) is a high-performance blockchain that stands out for its unique focus on scalability and efficiency. Initially created by the team behind Telegram, this network aims to provide a robust infrastructure for decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts.
With a design focused on speed and the ability to process large volumes of transactions, TON is effectively a solid alternative to other popular blockchains, offering solutions to address the scalability issues faced by traditional networks such as Ethereum.

What is The Open Network (TON)?
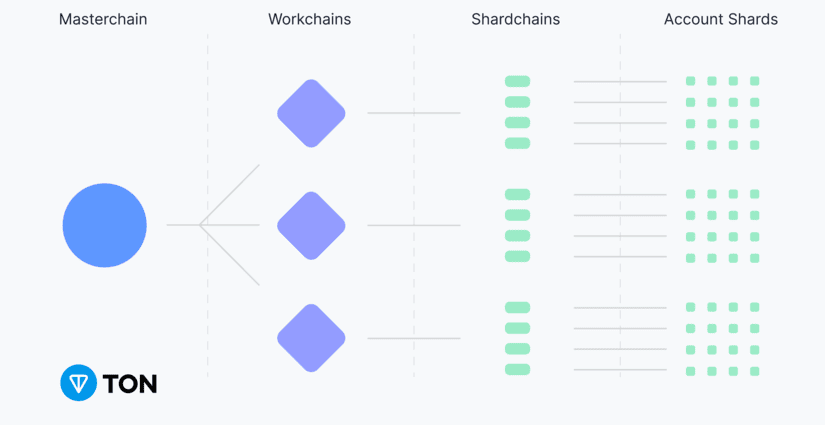
The Open Network (TON) is a blockchain designed to offer solutions to the scalability and efficiency issues in decentralized networks. It employs a multichannel architecture that allows for parallel execution of smart contracts and simultaneous processing of transactions.
Its ability to scale horizontally is achieved through sharding, dividing the network into independent segments called “shards,” each of which manages a portion of the network’s total load. This structure allows for increased processing capacity without compromising the overall performance.
TON stands out for its speed and resource optimization. It is designed to be highly interoperable, allowing for connections with other networks and decentralized systems, making it a flexible platform for the development of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts.
Multichannel Architecture
TON is distinguished by its multichannel design, which allows multiple smart contracts to be executed and transactions to be processed in parallel. This structure is complemented by the use of sharding, a division technique that fragments the network into “shards” or segments, each of which manages its own set of data and validators. This enables the blockchain to scale horizontally: as the load increases, processing capacity grows by adding more shards, without compromising the overall network performance.
Consensus Mechanism: Proof of Stake (PoS)
TON implements a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism that ensures the security of the network and prevents high energy consumption. Unlike systems such as Proof of Work (PoW), it allows validators to be selected based on the amount of tokens they have staked, which not only encourages active participation in the network but also reduces the energy costs associated with transactions.
TON Virtual Machine (TVM)
The TON Virtual Machine (TVM) is an essential component for executing smart contracts. It is an optimized execution environment designed to offer high performance, enabling contracts to be executed with low computational costs and high speed. This virtual machine is specifically designed to take full advantage of the network’s infrastructure, making it more efficient compared to other platforms like the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Resource Optimization and Low Latency
Transactions are executed with low latency, providing a smooth and fast user experience, even in applications that require high transaction volumes. This low latency is essential for applications such as instant payments or DeFi systems that rely on rapid transaction validation.
Interoperability
One of TON’s strengths is its ability to connect with other blockchains. Through bridges, it enables the transfer of data and assets between different decentralized platforms. This facilitates the creation of interconnected applications, promoting a global network of interoperability between different blockchain infrastructures.
Strengths and Areas for Improvement
TON is unique due to its horizontal scalability, allowing it to handle high transaction volumes. It is resilient to failures and enables the development of decentralized applications (dApps) with lower operational costs.
However, although TON presents innovative features, it must overcome several challenges. Firstly, network adoption is still limited compared to more established blockchains, such as Ethereum and Bitcoin, which could hinder its growth. Furthermore, implementing new applications may be complex for novice developers due to the need to understand its TVM, which adds a learning curve that complicates development.
Another aspect to consider is its origin linked to Telegram, which might generate mistrust among some users who prefer a completely decentralized approach, without reliance on a single entity. Lastly, although its scalability is an advantage, it faces fierce competition from other projects that also aim to solve performance and efficiency issues, such as Polkadot, Solana, or Avalanche.

What Toncoin is used for? The Native Token of TON
Toncoin (TON) is the native token of The Open Network (TON) and plays a crucial role within its ecosystem. Used for various functions within the network, Toncoin facilitates both the operation of the blockchain and participation in its governance.
USES AND FUNCTIONS:
Toncoin is primarily used to pay transaction fees within the network, ensuring the execution of smart contracts and the sending of payments. Additionally, validators who maintain the network’s security are incentivized through the token, making it an essential component of the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus system. Users can stake their tokens to participate in the validation process and earn rewards.
REWARDS AND GOVERNANCE:
Toncoin also plays a role in the decentralized governance of the blockchain. Through staking, users can influence decisions related to the evolution of the network, such as protocol changes or important updates. This allows the community to have an active role in decision-making.
SCARCITY AND CONTROLLED ISSUANCE:
Toncoin has a predefined initial supply, ensuring a controlled scarcity of tokens. This feature sets it apart from other tokens of popular blockchains that may have inflationary supplies. The issuance mechanism is designed to be sustainable, avoiding overissuance of tokens that could lead to devaluation of the currency in the long term.

Conclusion
Blockchain technology continues to evolve rapidly, and The Open Network (TON) emerges as a robust and adaptable option for those seeking scalable, fast, and efficient solutions. Its innovative architecture provides a balance between performance and energy sustainability, distinguishing it from many other blockchain solutions.
Although TON must compete in a space saturated with alternatives and still needs to overcome adoption barriers, its relationship with Telegram and its capabilities position it as one of the most promising options with the right tools to meet current demands, adapt, and evolve to solve future problems