The BOSS (Bitcoin Operational Standard System) framework is a new solution that aims to enhance the capabilities of the Bitcoin network. The system is designed with a one-of-a-kind meta-indexing structure that employs a uniform tagging method for transactions, based on Ordinals. This system establishes trust through the Bitcoin peer-to-peer protocol and the Ordinals indexing system.
By combining the concept of smart inscriptions with its components, BOSS is initiating a technical revolution in the Bitcoin blockchain, also known as the Timechain, opening up new opportunities for developers, investors, and users.
So, in this article we will look at what BOSS is and why it has the potential to take Bitcoin and the blockchain to the next level. The community believes this could be the foundation for a new generation of decentralized applications built on and for the Bitcoin network.
What is the Bitcoin Operational Standard System?

BOSS is a framework that enables advanced smart contracts, complex transactions, and decentralized applications on the Bitcoin blockchain. It leverages the power of Bob, a JavaScript Virtual Machine, to observe and execute special commands on the Bitcoin network.
It also introduces standards and protocols for code evolution and governance, such as OCV and ODE, which allow users to propose and vote on system improvements. The standard aims to bring the best features of other blockchain platforms to Bitcoin while maintaining its security, scalability, and resilience. This is a step towards the realization of the Godchain, a universal and trust-minimized blockchain system.
What Problems Does BOSS Solve?
- Lack of programmability: Bitcoin’s scripting language is limited and restrictive, making it difficult to create complex and flexible smart contracts and applications on the Bitcoin blockchain. BOSS introduces Bob, that can spot and implement special commands on the Bitcoin grid, enabling advanced computations and interactions.
- Lack of standardization: Bitcoin’s ecosystem lacks a common set of rules and protocols for creating and deploying smart contracts and applications. This leads to fragmentation, inconsistency, and inefficiency. BOSS proposes standards such as OCV and ODE, which provide a framework for code evolution, governance, and interoperability.
- Lack of innovation: Bitcoin’s ecosystem is often overshadowed by other blockchain platforms that offer more features and capabilities, such as Ethereum’s dApps and DeFi services. BOSS aims to bring the best of both worlds, leveraging the security and resilience of Bitcoin while enabling similar functionalities and more on its network.
What is BOB, Bitcoin Virtual Machine?
Bob is more than a virtual machine; it is also a Bitcoin observer that can communicate and interact with the Bitcoin blockchain in a novel way. Think of it like an AI whose purpose is to facilitate interactions between the users and the blockchain. It monitors the blockchain and executes specially formatted JavaScript instructions, called OSS Inscriptions, that enhance Bitcoin’s secure and reliable infrastructure.
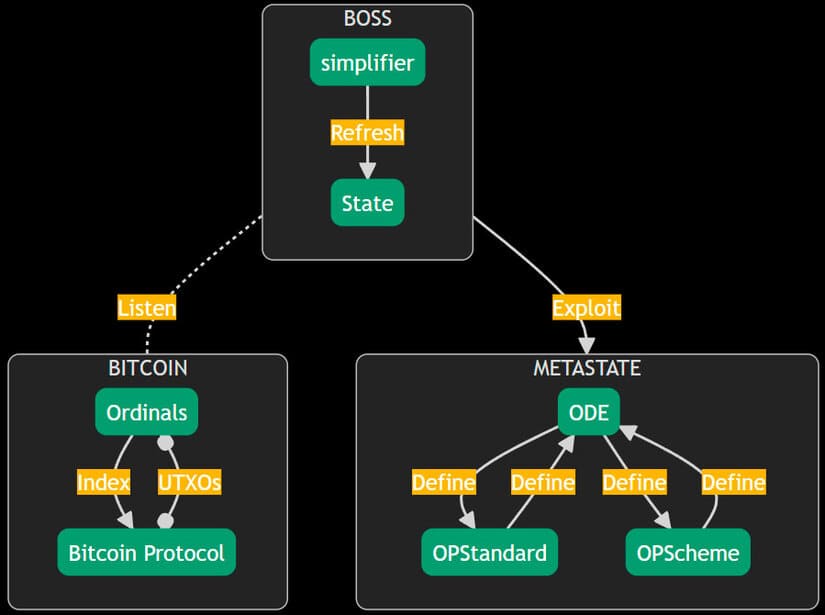
Bob operates with three fundamental components, OSS Inscriptions, OPSchemes, and OPStandards. Users send JavaScript commands, known as OSS Inscriptions, to Bob via Bitcoin transactions.
These commands follow specific formats, called OPSchemes, and adhere to a set of rules defined by the OPStandards. Bob receives these commands and executes them accordingly.
It observes the Bitcoin blockchain, detects and executes these commands, and updates its internal state accordingly. Bob is also flexible and adaptable, as users can propose changes to the OPStandard using TDTDs.
Moreover, Bob interacts with other components of BOSS, such as Odes and OCV, to enable decentralized governance and code evolution. Bob is a powerful platform that brings more functionality and programmability to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Operational Commit for Voting (OCV)
The BOSS framework is a complex system that relies on standards to ensure smooth and efficient operation. One of these standards is the Operational Commit for Voting (OCV), which plays a central role in enabling decentralized decision-making within the ecosystem. OCV facilitates operation commits, similar to code updates in software development, but decided through a democratic, decentralized voting process.
This allows an iterative, evolutionary process where proposed commits can introduce new features, fix bugs, or enhance existing functionalities. The adaptability and universality of OCV make it a key component of the BOSS framework.
The BOSS ecosystem is built on Operational Decentralized Entities (Ode), which are its first standard in the OCV series, also known as OCV0. Ode establishes the groundwork for building applications on top of Bitcoin and is a resilient Bitcoin entity that maintains its cohesiveness over time through a built-in governance framework.
Operational Decentralized Entities (ODEs)
Built on the Bitcoin Operational Standard System (BOSS), Operational Decentralized Entities (ODEs) are a breakthrough in blockchain-based systems development. They harness the power of the Bitcoin blockchain and create new possibilities for its applications. ODEs are composed of various stakeholders who share a common goal: to oversee the evolution of a standard protocol definition.
ODE is a low-level, permissionless, on-chain protocol governance standard that enables BOSS. It is supported by Oshi and TheOrd team. It allows for changes to be made to existing on-chain protocols within BOSS and beyond, such as Ordinals. Trust in BOSS is based on the community consensus on the definition of protocols.
Simplifiers are responsible for integrating these distributed protocols. They act as agents who execute compatible transactions. ODE defines how changes are applied to OPStandard or any other protocol that follows OPScheme (i.e., in the meta registry). This ensures decentralized (since on-chain) and transparent governance of operational protocols.
ODE is essential for governing operational protocols within BOSS. It also contributes to academic research on operational protocol governance. By explaining how changes are made to operational protocols, ODE enables the investigation of decentralized and transparent governance issues.
What is the Godchain and The God Protocol?
BOSS, Bob, OPStandard, and OCV are the four components that form a decentralized ecosystem called the Godchain. This name reflects the vision of a system that is fully decentralized and trust-minimized, built on the Bitcoin blockchain, and able to observe every action as closely as possible to the moment.
The God Protocol is a general concept of a set of computer protocols that could act as a perfect third party for any process that involves an exchange of value between two or more independent parties. This third party would be unbiased, error-free, and privacy-preserving.
It would also be equally accessible to all participants, execute actions according to mutually pre-agreed-upon rules and commands, and not leak sensitive information to unintended entities.
Why can BOSS Revolutionize the Bitcoin Blockchain?
If BOSS moves from the theoretical realm and becomes a reality, it would become, by far, the most important and massive upgrade to the Bitcoin Blockchain since its inception. BOB, OCV, and ODE are designed to give the users complete control, and improve experience on the blockchain.
Can BOSS dethrone Ethereum?
Since its hasn’t move beyond the proposal stage, it is impossible to determine if BOSS can dethrone Ethereum as the prefer Blockchain for new projects. However, there are some aspects in which BOSS can be better than Ethereum:
- Security: BOSS leverages the robust and secure infrastructure of Bitcoin, which has proven to be resilient against attacks and tampering. Ethereum, on the other hand, has faced several security breaches and vulnerabilities in its history, such as the DAO hack and the Parity multisig wallet bug.
- Scalability: BOSS utilizes the Taproot upgrade, which enhances transaction flexibility and privacy on Bitcoin. Taproot makes complex transactions indistinguishable from standard ones, reducing the size and cost of transactions. This could improve the scalability and efficiency of BOSS compared to Ethereum, which suffers from high fees and congestion due to its limited capacity.
- Adaptability: BOSS is designed to be an evolving and adaptable system, where users can propose and vote on code updates and improvements using the OCV standard and the ODE framework. This allows BOSS to incorporate new features and functionalities over time, keeping pace with the changing needs and demands of the community. Ethereum, while also having a governance process, faces challenges in reaching consensus and implementing changes due to its size and diversity.
Conclusion
BOSS is a revolutionary framework that enables advanced applications and services on the Bitcoin blockchain. By leveraging Bob, the JavaScript Virtual Machine, it offers unprecedented capabilities and flexibility to developers and users. Also introduces standards and protocols, such as OCV and ODE, that facilitate decentralized governance and code evolution.
BOSS aims to bring the best features of other blockchain platforms, such as Ethereum, to the Bitcoin ecosystem, while maintaining its security and scalability. It is not a static system, but an evolving one, driven by the participation and innovation of its community.
BOSS is a step towards the realization of the Godchain, a universal and interoperable blockchain system. It could be the future of Bitcoin and blockchain technology.










