The fact that banks do not like cryptocurrencies is not something that surprises anyone. If someone sees that their power to manage money at will is at risk, they will at least show a bit of nervousness, that on July 17 resulted in a statement from the bank of international payments (BIS) expressing its opinion on cryptocurrencies.
“A good way to examine whether a new technology can be a truly useful addition to the existing monetary landscape is to step back and review the fundamental roles of money in an economy and what history teaches us about failed attempts to create new private moneys. Then one can ask whether money based on this new technology can improve upon the current monetary landscape in any way”
FIDUCIARY MONEY
According to the BIS, fiduciary money has three fundamental functions:
- A unit of account.
- A medium of exchange.
- A store of value.
And after a brief review of the history of money and how banks have been the driving force of international trade and economic activity in general or how independent central banks say they have largely achieved the goal of safeguarding the economic and politic interests of society in a stable currency, the BIS began its analysis of cryptocurrencies.
Given the current economic situation, it is surprising that central banks can claim success based on their monetary policies, which have left several nations in a precarious situation, such as the case of Greece, where more than 30 privatizations of the public stock market took place at the price of balance of foreign helps to pay a questionable debt deriving the national sovereignty to private companies.
It is also surprising that fiduciary money is characterized as a reserve of value since there is currently no endorsement of any type of asset as was formerly gold. The only current value is the trust between the parties.
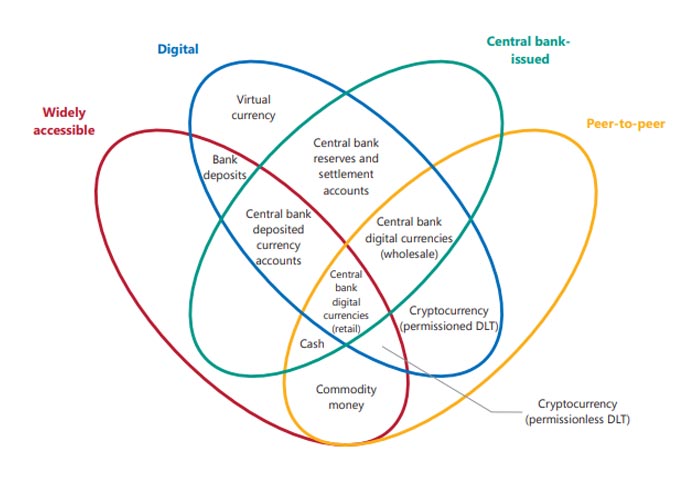
In this image we can see the Money Flower, which distinguishes four key properties of money: the issuer, the form, the degree of accessibility and the payment transfer mechanism.
CRYPTOCURRENCIES
The cryptocurrencies are composed by three elements:
- A set of rules (the “protocol”).
- A ledger (to store the transaction history).
- A decentralized network
The Money Flower combine three characteristics:
- They are digital.
- Its value depends on the interest of the users.
- They allow Peer-to-Peer exchange.
Comparing cryptocurrencies with other digital forms of payment they state:
“Cryptocurrencies aspire to be a new form of currency and promise to maintain trust in the stability of their value through the use of technology. Compared with other private digital moneys such as bank deposits, the distinguishing feature of cryptocurrencies and digital bank accounts is that these have been around for decades… And privately issued “virtual currencies” – eg as used in massive multiplayer online games like World of Warcraft – predate cryptocurrencies by a decade.”
It is true that the issuance of virtual currencies has been taking place for decades, as indicated by this quote, however the simple comparison of these digital currencies used in online games with a cryptocurrency has no meaning due to the centralized nature and underlying technology has nothing to do with blockchain technology and the way in which distributed money works.
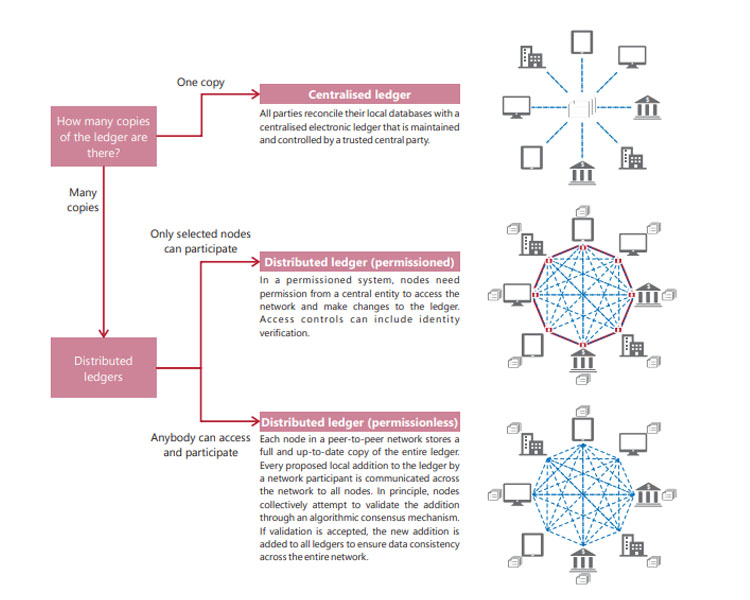
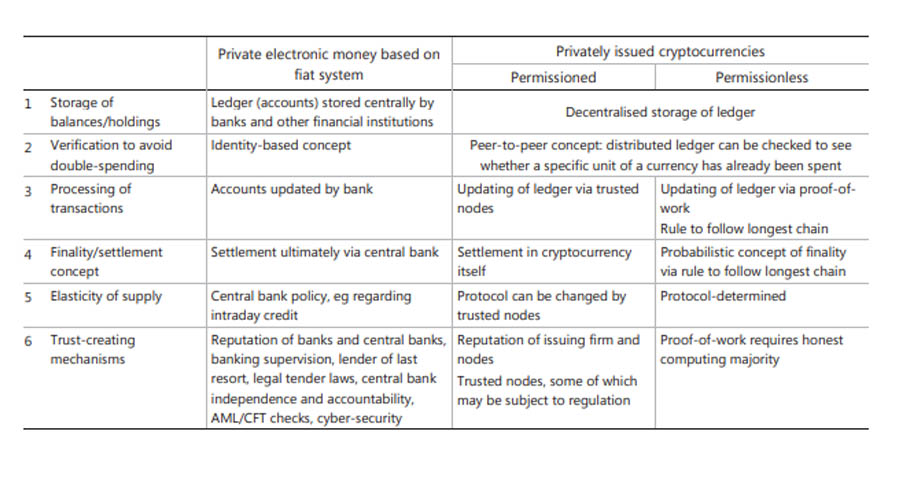
CENTRALIZED LEDGER / PERMISSIONED / PERMISSIONLESS
LIMITATIONS OF CRYPTOCURRENCIES
According to the BIS, the limitations of cryptocurrencies are:
- A high energy cost.
- Scalability
- Value stability.
- Confidence in the firmness of payments.
“In general, decentralized cryptocurrencies suffer from a series of deficiencies,” stated the Bank of international payments.
Reading the limitations that cryptocurrences have according to BIS gives the feeling that they have not made an exhaustive study of the intrinsic characteristics of cryptocurrencies because there are numerous projects that have managed to solve the limitations raised by themselves previously.
UNDERLYING TECHNOLOGY.
Cryptocurrencies as a form of payment is not something that is attractive banks. The technology behind it sees it with a different approach, and as they say, it can be promising in other fields, such as for cross-border transfers or the use of Smart Contracts.
REGULATORY CHALLENGES POSED BY CRYPTOCURRENCIES
- Money laundering (AML).
- Combating the financing of terrorism (CFT).
“Events such as Bitcoin’s strong market reaction to the shutdown of Silk Road, a major marketplace for illegal drugs, suggest that a non-negligible fraction of the demand for cryptocurrencies derives from illicit activity”
- Consumer protection.
- Fraud protection.
“A recent communiqué of the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors highlights issues of consumer and investor protection, market integrity, tax evasion and AML/CFT, and calls for continuous monitoring by the international standard-setting bodies. It also calls for the Financial Action Task Force to advance global implementation of applicable standards.”
It seems that both Fiat and cryptocurrencies have very similar problems, since money laundering, financing of terrorism, fraud etc, have always been with us. It would be convinient that instead of looking for problems in cryptocurrencies, if they focus their efforts on solving their own.