With the rise of digital payment systems and mobile wallets, universal financial inclusion is now possible. Systematic barriers such as outdated payment infrastructures and challenges to interoperability are now being solved through emerging technologies, like blockchain and crypto.
But today’s global financial system still does not meet the needs of unbanked people, especially in Africa, the Middle East, Latin America, East, and Southeastern Asia. The reason is that current payment systems are not interoperable.
To make digital payment systems interoperable, Mojaloop kicks in.
What is Mojaloop?
Mojaloop is an open-source software platform that aims to improve the interoperability of payment systems, making it easier and more affordable to send and receive money, especially in emerging markets. Mojaloop, launched in May 2020, is managed by Mojaloop Foundation, a charitable nonprofit organization based in Wakefield, Massachusetts.
In essence, Mojaloop is designed to provide a reference model for payment interoperability, that can be used to overcome barriers that have slowed the spread of digital financial services. It is not a financial product or application in itself. According to Mojaloop Foundation, it is an open-source blueprint that will remove barriers like time, money, and technical complexity, that have hindered payment models from meeting the digital financial needs of the world’s 1.7 billion unbanked people.
Mojaloop grew out of principles set forth by the Financial Services for the Poor team at the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Global payment network Ripple is also closely related to Mojaloop Foundation.
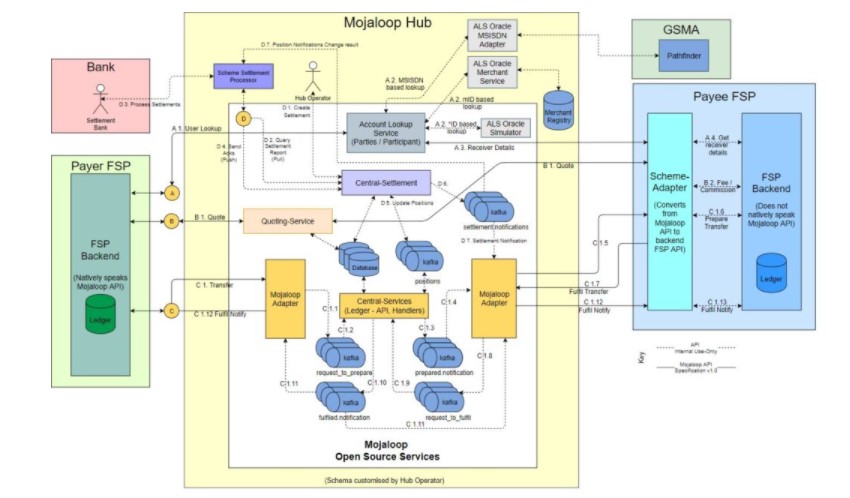
What is Inside Mojaloop Hub?
There are several components that make up the Mojaloop ecosystem. According to the Mojaloop documentation, the Mojaloop Hub is the primary container and reference used to describe the core Mojaloop components. The Mojaloop is further split into two domains: Mojaloop Hub and Mojaloop Open-Source services.
The Moojaloop Hub consists of Mojaloop API Adapters, the Account Lookup Service (ALS), the Central Services (CS), Central Settlement service, and Quoting Service.
Mojaloop API Adaptors
According to the documentation provided by Mojaloop, the Mojaloop API Adapters provide the standard set of interfaces a digital financial service provider (DFSP) can implement to connect to the system for transfers.
A service provider can connect with Mojaloop by adapting Mojaloop’s example code or implementing the standard interfaces into their own software. This provides a simple way for a DFSP to connect to the interoperable network.
Central Services (CS)
The central services contain a set of components required to move money from one DFSP to another through the Mojaloop API Adapters like banks or clearinghouses.
This contains not only the core central ledger logic to move money, but also provides fraud management services, identity lookup, and enforce scheme rules.
Account Lookup Service (ALS)
This component routes each payment to the correct service provider in the ecosystem. The Mojaloop documentation explains this service as:
“The Account Lookup Service (ALS) provides a mechanism to resolve FSP routing information through the Participant API or orchestrate a Party request based on an internal Participant look-up. The internal Participant lookup is handled by a number of standard Oracle adapter or services. Example Oracle adapter/service would be to look-up Participant information from Pathfinder or a Merchant Registry. These Oracle adapter or services can easily be added depending on the schema requirements.”
Quoting Service
The quoting service determines fees and commission required to perform a financial transaction between two DFSPs. This service is always set up between payer FSP to Payee FSP, just like a financial transaction.
Central Settlement Services
The Central Settlements service exposes the Mojaloop settlement API to manage the settlements between FSPs and the Central Hub. It also manages Settlement Windows and Settlements Event Triggers and provides information about FSPs accounts and settlements.

How Does It work?
A digital financial service provider (DFSP) can implement standard interfaces into its software or adapt an example code to connect to the network. Once connected, a set of central services provides a hub through which money can flow from one DFSP to another. The Mojaloop Hub manages all other activities like ID verification and fraud management.
What Mojaloop Tries to Deliver?
The Mojaloop Foundation adheres to a set of eight principles that it believes are required for payment systems to be inclusive. Thee principles include open-loop interoperability between DFPS, a push payments model with immediate funds transfer and same-day settlement, a system-wide shared fraud and security protection, efficient identity and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements and more.
By keeping these prinicples in mind, the Mojaloop team is creating an open-source platform where organizations can create interoperable digital payment systems to increase financial inclusion.
Important Links
- Mojaloop website: https://mojaloop.io/
- Mojaloop Documentation: https://docs.mojaloop.io/documentation/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/mojaloop
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/mojaloop