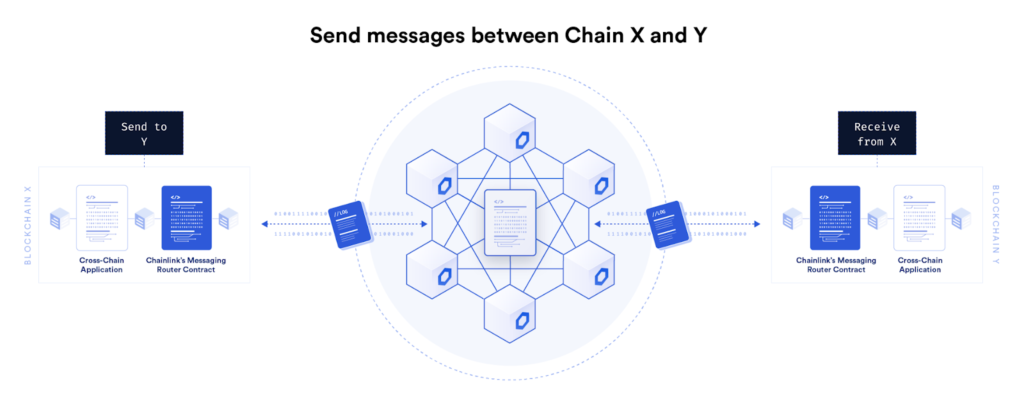
Chainlink, the leading decentralized oracle network, has introduced a new Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) that will allow smart contracts to interoperate across blockchains for messages, commands, and tokens.
According to a blog post by Chainlink on Thursday, August 5, Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) is a new open-source standard for cross-chain communication that will help the creation of advanced Dapps. CCIP aims to establish a universal connection between hundreds of blockchain networks by providing smart contract developers “a generalized, compute-enabled infrastructure for transferring data and smart contract commands across blockchain networks.”
Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) sits within a layered open-source technology stack and underpins a variety of cross-chain services, such as the Chainlink Programmable Token Bridge and an anti-fraud network.
The Programable Token Bridge is the most anticipated feature of CCIP technology. According to the blog post, the Programmable Token Bridge is a reference bridge implementation built upon the CCIP. It is a unified bridge system, where various bridge connections between chains are secured by unique committees of nodes. The blog post reads:
“The Programmable Token Bridge is compute-enabled, empowering users and smart contracts to send not only their tokens but also commands to the bridge and have it run customized logic around how it interacts with other blockchains. Users don’t need to know how to use other blockchains—they just need to send instructions to the bridge on how they want to interact with other chains, and the bridge will automatically move the tokens cross-chain and deploy them in smart contracts on the destination chain within an atomic transaction.”
According to Chainlink, CCIP tech stack also features a newly invented risk management system never before seen in the blockchain industry called the Anti-Fraud Network. The sole purpose of this Anti-Fraud Network is to monitor CCIP services for malicious activity that could lead to financial loss. The network will contain a separate fully independent committees of nodes than the committee monitoring CCIP services.
Chainlink describes the working of Anti-Fraud Network as:
“The Anti-Fraud Network acts as a verification layer and will periodically submit heartbeat checks when the system is operating as normal. If the Anti-Fraud Network’s heartbeat messages stop or its nodes notice any nefarious activity, an emergency shutdown is automatically triggered to stop a particular cross-chain service. The pause allows user funds to be protected against a potential black swan event affecting the service.”
In short, the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) is the part of a layered open-source tech stack that contains the CCIP itself, a generalized protocol that supports the delivery of any type of data that a smart contract may want to deliver across chains, a Programable Token Bridge, an Anti-Fraud Network, and other cross-chain services. The overall focus of Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) is to build a new global standard for decentralized inter-blockchain messaging, data and token movements.
Celsius Network, a CeFi lending platform with $16B+ in digital asset holdings and 800k+ users, has already announced it plans to use CCIP within its yield generation activities.
If you found this article interesting, here you can find more Chainlink News