The inception of the Ethereum blockchain in 2015 started a whole new era for blockchain technology. The introduction of smart contract functionality to the blockchain proved to the world that the technology is much more capable than originally thought.
After 5 years, Ethereum is still dominating the blockchain space. Hundreds of thousands of projects are now providing their services on Ethereum, and more is coming. But, just like its predecessor Bitcoin, Ethereum does not offer much scalability and interoperability to this space.
Due to the recent DeFi boom, the Ethereum network is now busier than ever. The situation has further degraded the performance of the network. So, high gas fees, scalability, and interoperability issues have forced projects to look for alternatives.
Among other choices, Polkadot is also getting popular among businesses due to its unique design and features. Polkadot is now considered as a direct rival to Ethereum. So what is it?
What is Polkadot Blockchain?
Polkadot is an open-source project founded by the Web3 Foundation to deliver the most robust platform for security, scalability, and innovation. The project is a brainchild of Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood and former head of security in the Ethereum Foundation Jutta Steiner. As reported, the network went live on mainnet in May of 2020.
Polkadot is the next-gen blockchain platform developed together by Web3 Foundation, Parity Technologies, ChainSafe, Soramitsu, and Polkadot JS.
Polkadot Architecture
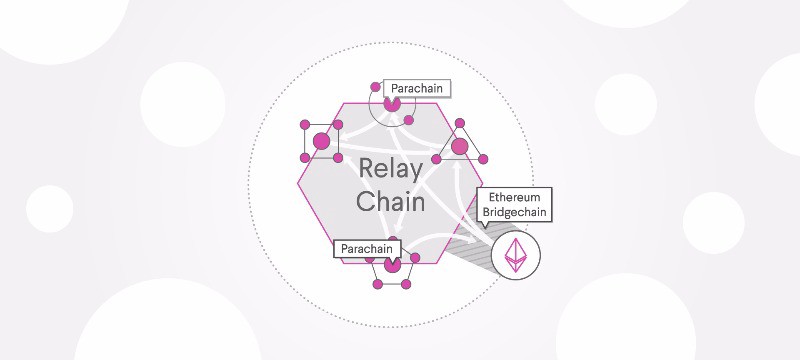
Polkadot uses a novel hybrid consensus algorithm called GRANDPA/BABE which is a flavor of Proof-of-Stake (PoS), specially tailored for Polkadot. The most critical parts of the Polkadot network are Relay Chain, Parachains, Parathreads, and Bridges.
Relay Chain: Relay Chain is the main core of Polkadot and the main communication hub between parachains. It is the central chain of Polkadot where all validators are staked on the Relay Chain in the native token, DOT, and validate for the Relay Chain. According to the developer, the Relay Chain has deliberately minimal functionality. For instance, it does not support smart contracts. The main responsibility is to coordinate the system as a whole.
Parachains: Parachains are independent blockchains running on top of Relay Chain. Every Parachain provides chain-specific features to the Polkadot network and enjoys the shared security of Relay Chain. One Parachain will be providing smart contract functionality, another chain will provide a stable coin for payments between chains.
Parachains are managed by collators—sit atop parachains and maintain a full-node for the Relay Chain—that collect parachain transactions from users and produce state transition proofs for validators. But there is always a limited number of Parachains on the network. Parachain candidates compete in the public auction to obtain their slot on the Relay Chain.
Parathreads: These are similar to Parachains but, unlike Parachain where candidates get their through auction, candidates can get a slot instantly but for a very short time. Parathreads allow projects to have a taste of Polkadot before purchasing an expansive parachain slot.
Bridges: Bridges provide interoperability functionality which allows for transfers of tokens between Polkadot and outside networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Standout Features
Scalability: According to its website, the network provides unprecedented economic scalability by enabling a common set of validators to secure multiple blockchains. As Polkadot is a sharded multichain network, it can process many transactions on several chains in parallel, unlike legacy blockchain networks that process transactions one-by-one.
Interoperability: Polkadot enables cross-chain transfers of any type of data or asset, not just tokens. Connecting to Polkadot gives projects the ability to interoperate with a wide variety of blockchains (Parachains) in the Polkadot network.
A Cross-Chain Messaging Protocol (XCMP) provides parachains a trustless environment for a verifiable message transfer that enables real interoperability.
Forkless: Perhaps, one of the real standout feature of Polkadot is that it does not require hard forks to upgrade or make major changes on the platform. Polkadot has taken a completely new approach to decentralized network development by not trying to develop the whole world on top of a single blockchain.
Custom Blockchain Development: Polkadot provides a simple software development kit (SDK) called Substrate to create a custom blockchain in minutes. The blockchain made through Substrate will be natively compatible with Polkadot. According to Substrate’s website, 129 teams are currently building customized blockchains on Substrate, ranging from DeFi to gaming, decentralized Identity, and more.
DOT Token: According to the Polkadot website, the DOT token serves three key functions: providing governance for the network, operating the network through staking, and creating parachains by bonding DOT.
Bonding parachain is a unique purpose that DOT serves. When a new parachain is added to Polkadot Relay Chain, the DOT tokens are locked during their bonding period and released back to the account that bonded them after the duration of the bond has elapsed and the parachain is removed.
Conclusion
The Polkadot ecosystem is growing larger and more and more teams are deploying or migrating their projects to Polkadot. Many of them are coming from Ethereum. By bringing multiple specialized chains together into one scalable network, Polkadot is promising blockchain technology to reach its full potential for real-world use cases.
As reported, Ethereum 2.0 has started its rollout but it has still a long way to go. It will be interesting to see how these two blockchains compete in the future.
Important Links
Polkadot Website: https://polkadot.network/
Polkadot Twitter: https://twitter.com/Polkadot
Polkadot Documentation: https://wiki.polkadot.network/docs/en/learn-collator
Web3 Foundation: https://web3.foundation/
Parity Technologies: https://www.parity.io/
Substrate: https://www.substrate.io/